来源:N Engl J Med. 2021 May 6;384(18):1691-1704. 906
Mark A Mintun, Albert C Lo, Cynthia Duggan Evans, Alette M Wessels, Paul A Ardayfio, Scott W Andersen, Sergey Shcherbinin, JonDavid Sparks, John R Sims, Miroslaw Brys, Liana G Apostolova, Stephen P Salloway, Daniel M Skovronsky
Background: A hallmark of Alzheimer's disease is the accumulation of amyloid-β (Aβ) peptide. Donanemab, an antibody that targets a modified form of deposited Aβ, is being investigated for the treatment of early Alzheimer's disease.
Methods: We conducted a phase 2 trial of donanemab in patients with early symptomatic Alzheimer's disease who had tau and amyloid deposition on positron-emission tomography (PET). Patients were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to receive donanemab (700 mg for the first three doses and 1400 mg thereafter) or placebo intravenously every 4 weeks for up to 72 weeks. The primary outcome was the change from baseline in the score on the Integrated Alzheimer's Disease Rating Scale (iADRS; range, 0 to 144, with lower scores indicating greater cognitive and functional impairment) at 76 weeks. Secondary outcomes included the change in scores on the Clinical Dementia Rating Scale-Sum of Boxes (CDR-SB), the 13-item cognitive subscale of the Alzheimer's Disease Assessment Scale (ADAS-Cog13), the Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study-Instrumental Activities of Daily Living Inventory (ADCS-iADL), and the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE), as well as the change in the amyloid and tau burden on PET.
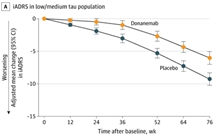
Results: A total of 257 patients were enrolled; 131 were assigned to receive donanemab and 126 to receive placebo. The baseline iADRS score was 106 in both groups. The change from baseline in the iADRS score at 76 weeks was -6.86 with donanemab and -10.06 with placebo (difference, 3.20; 95% confidence interval, 0.12 to 6.27; P = 0.04). The results for most secondary outcomes showed no substantial difference. At 76 weeks, the reductions in the amyloid plaque level and the global tau load were 85.06 centiloids and 0.01 greater, respectively, with donanemab than with placebo. Amyloid-related cerebral edema or effusions (mostly asymptomatic) occurred with donanemab.
Conclusions: In patients with early Alzheimer's disease, donanemab resulted in a better composite score for cognition and for the ability to perform activities of daily living than placebo at 76 weeks, although results for secondary outcomes were mixed. Longer and larger trials are necessary to study the efficacy and safety of donanemab in Alzheimer's disease. (Funded by Eli Lilly; TRAILBLAZER-ALZ ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT03367403.).
免责声明:相关信息仅限药物研发参考使用,本网站不保证信息真实和准确!
关注“药研苑”公众号,查看前景解析。

|
推荐阅读: ・2025年1-3季度口崩片市场哪个强? ・2025年1-3季度口溶膜制剂哪家强? ・免疫检查点抑制剂,谁将成为下一个王者? ・质子泵相关抑酸类药物市场即将回暖 ・中药1类新药距离封神还有多远 |
|
“药品营销避坑”试读: ・药品立项需要注意什么(一) ・药品生命周期管理(一) ・改剂型,口服液体制剂“金矿”还是“陷阱 |
我们提供如下咨询服务:药品信息发布、药品立项、市场前景分析、医院及药品零售市场分析、药品市场调研及制定推广策略、国外药品引进、国内批文转让、上市前后临床试验设计、药品彩页及主图设计、药品推广PPT制作。您可以关注公众号“药研苑”后,在主页面发送消息,咨询相关服务。


2024年10月29日,礼来Eli Lilly宣布Donanemab(商品名:Kisunla)TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 6研究3b期临床试验取得积极结果。
发布日期:2024-10-29 浏览数:1450
2023年7月17日Eli Lilly公布了抗β淀粉样蛋白(Aβ)单克隆抗体Donanemab的3期临床试验TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 2试验结果。试验显示 Donanemab能够有效改善Aβ斑块检测阳性阿尔茨海默症早期症状患者的认…
发布日期:2023-07-17 浏览数:1416

2024年7月2日,礼来公司宣布FDA批准Donanemab(商品名Kisunla™)350 mg/20 mL,每月一次静脉输注用于治疗处于轻度痴呆阶段,伴有轻度认知障碍(MCI),并经淀粉样蛋白病理学确诊的成人早期症状性…
发布日期:2024-07-02 浏览数:1162
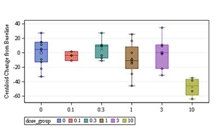
Intravenous donanemab 10 mg/kg can reduce amyloid deposits in AD despite having a shorter than expected half-life.
发布日期:2021-02-14 浏览数:1136
 改变滴定方案礼来降低其阿尔茨海默症抗体药物脑水肿发生率
改变滴定方案礼来降低其阿尔茨海默症抗体药物脑水肿发生率横切线®为注册商标
Copyright 2020 横切线®药研苑 备案号:粤ICP备18041379号-3